|
1 | 1 | --- |
2 | 2 | Title: 'Box Model' |
3 | | -Description: 'The Box Model is a CSS layout mechanism that the web browser uses to render content organized by box-shaped elements. Each element is made of four specific areas: - width and height: The width and height of the content area. - padding: The amount of space between the content area and the border. - border: The thickness and style of the border surrounding the content area and padding. - margin: The amount of space between the border and the outside edge of the element. CSS Box Model Diagram This area contains the actual content of an element, including text and images. It also sometimes has a background-color or background-image.' |
| 3 | +Description: 'Defines how element dimensions and spacing are calculated on a webpage.' |
4 | 4 | Subjects: |
5 | | - - 'Web Development' |
6 | 5 | - 'Web Design' |
| 6 | + - 'Web Development' |
7 | 7 | Tags: |
8 | 8 | - 'Box Model' |
9 | | - - 'Padding' |
10 | | - - 'Borders' |
| 9 | + - 'CSS' |
| 10 | + - 'Positioning' |
11 | 11 | CatalogContent: |
12 | 12 | - 'learn-css' |
13 | 13 | - 'paths/front-end-engineer-career-path' |
14 | 14 | --- |
15 | 15 |
|
16 | | -The Box Model is a CSS layout mechanism that the web browser uses to render content organized by box-shaped elements. Each element is made of four specific areas: |
| 16 | +The **box model** is a fundamental concept in CSS that defines how element dimensions and spacing are calculated on a webpage. It treats every HTML element as a rectangular box consisting of four distinct areas: content, padding, border, and margin. Understanding the box model is essential for creating precise layouts, controlling element spacing, and achieving consistent visual designs across different browsers. |
| 17 | + |
| 18 | +The box model provides a standardized approach to calculating an element's total space on a page. It is used extensively in responsive web design, grid layouts, flexbox implementations, and any scenario where precise control over element dimensions and positioning is required. Web developers rely on the box model to create complex layouts, maintain visual consistency, and ensure elements display correctly across various screen sizes and devices. |
| 19 | + |
| 20 | +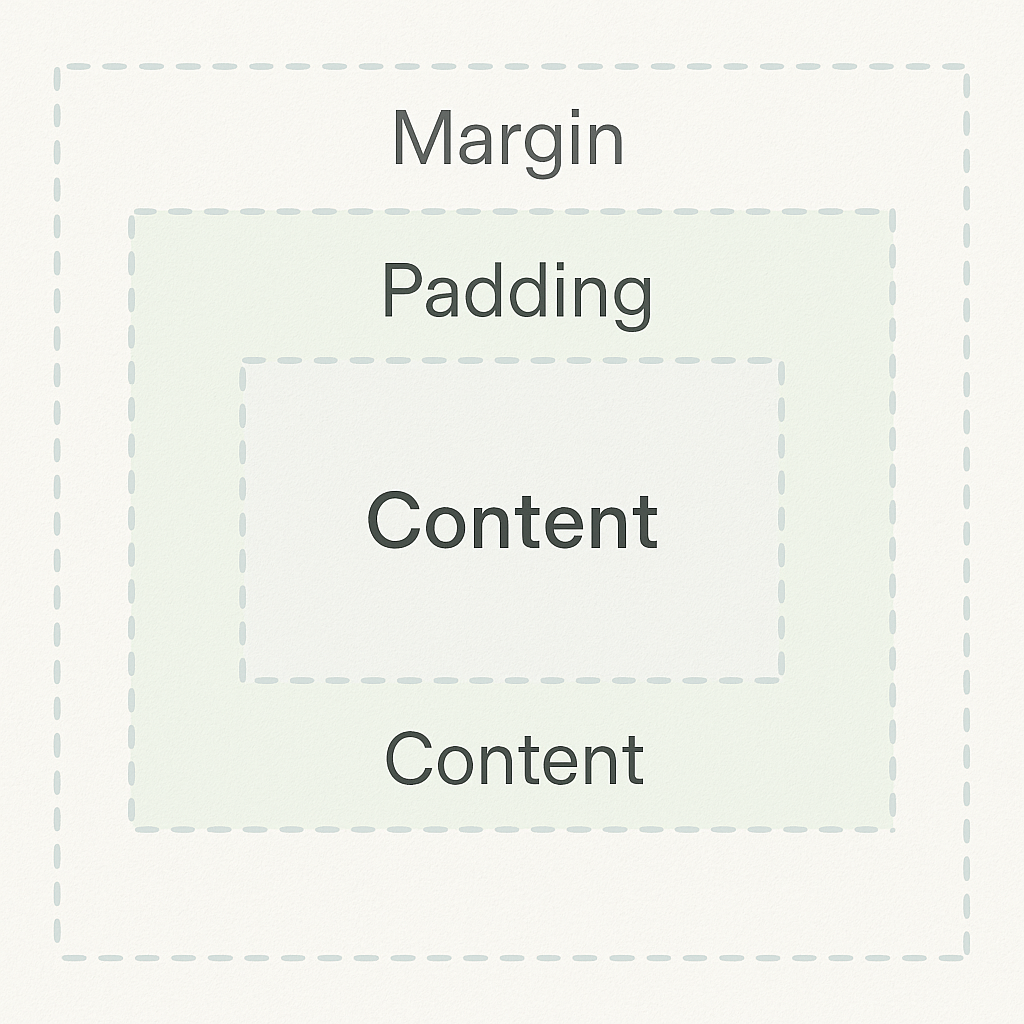 |
| 21 | + |
| 22 | +The box model can be controlled through various CSS properties: |
| 23 | + |
| 24 | +- `width`: Sets the width of the content area |
| 25 | +- `height`: Sets the height of the content area |
| 26 | +- `padding`: Controls the transparent space between content and border |
| 27 | +- `border`: Defines the line surrounding the padding and content |
| 28 | +- `margin`: Sets the transparent space outside the border |
| 29 | +- `box-sizing`: Determines how total width and height are calculated |
| 30 | + |
| 31 | +**Return value:** |
| 32 | + |
| 33 | +The box model doesn't return a value, as it's not a function — instead, it defines how an element's total size is calculated based on its content, padding, border, and margin. |
| 34 | + |
| 35 | +## Example 1: Basic Box Model Implementation |
| 36 | + |
| 37 | +The following example demonstrates the fundamental structure of the CSS box model with visible borders and spacing: |
| 38 | + |
| 39 | +```css |
| 40 | +.box-example { |
| 41 | + width: 200px; /* Content area width */ |
| 42 | + height: 100px; /* Content area height */ |
| 43 | + padding: 20px; /* Space around content */ |
| 44 | + border: 5px solid #333; /* Border around padding */ |
| 45 | + margin: 15px; /* Space outside border */ |
| 46 | + background-color: #f0f0f0; |
| 47 | +} |
| 48 | +``` |
| 49 | + |
| 50 | +```html |
| 51 | +<!DOCTYPE html> |
| 52 | +<html lang="en"> |
| 53 | + <head> |
| 54 | + <meta charset="UTF-8" /> |
| 55 | + <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> |
| 56 | + <title>Basic Box Model Example</title> |
| 57 | + <style> |
| 58 | + .box-example { |
| 59 | + width: 200px; |
| 60 | + height: 100px; |
| 61 | + padding: 20px; |
| 62 | + border: 5px solid #333; |
| 63 | + margin: 15px; |
| 64 | + background-color: #f0f0f0; |
| 65 | + } |
| 66 | + </style> |
| 67 | + </head> |
| 68 | + <body> |
| 69 | + <div class="box-example"> |
| 70 | + This content demonstrates the box model structure. |
| 71 | + </div> |
| 72 | + </body> |
| 73 | +</html> |
| 74 | +``` |
| 75 | + |
| 76 | +This generates the following output: |
| 77 | + |
| 78 | + |
| 79 | + |
| 80 | +In the above example, the total width calculation is: 200px (content) + 40px (left + right padding) + 10px (left + right border) = 250px. The margin adds an additional 30px of spacing around the element but doesn't contribute to the element's rendered size. The background color fills the content and padding areas, while the border creates a visible boundary. |
| 81 | + |
| 82 | +## Example 2: Responsive Card Layout |
| 83 | + |
| 84 | +The following example shows how the box model applies to real-world responsive card components commonly used in modern web design: |
| 85 | + |
| 86 | +```css |
| 87 | +.card { |
| 88 | + width: 100%; |
| 89 | + max-width: 300px; /* Responsive width constraint */ |
| 90 | + padding: 24px; /* Internal spacing for content */ |
| 91 | + border: 1px solid #ddd; /* Subtle border definition */ |
| 92 | + border-radius: 8px; /* Rounded corners */ |
| 93 | + margin: 16px auto; /* Center alignment with spacing */ |
| 94 | + background-color: white; |
| 95 | + box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1); |
| 96 | +} |
| 97 | + |
| 98 | +.card-title { |
| 99 | + margin: 0 0 12px 0; /* Remove top margin, add bottom spacing */ |
| 100 | + font-size: 1.25rem; |
| 101 | + font-weight: bold; |
| 102 | +} |
| 103 | + |
| 104 | +.card-content { |
| 105 | + margin: 0; /* Remove default paragraph margins */ |
| 106 | + line-height: 1.5; |
| 107 | + color: #666; |
| 108 | +} |
| 109 | +``` |
| 110 | + |
| 111 | +```html |
| 112 | +<!DOCTYPE html> |
| 113 | +<html lang="en"> |
| 114 | + <head> |
| 115 | + <meta charset="UTF-8" /> |
| 116 | + <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> |
| 117 | + <title>Responsive Card Layout</title> |
| 118 | + <style> |
| 119 | + .card { |
| 120 | + width: 100%; |
| 121 | + max-width: 300px; |
| 122 | + padding: 24px; |
| 123 | + border: 1px solid #ddd; |
| 124 | + border-radius: 8px; |
| 125 | + margin: 16px auto; |
| 126 | + background-color: white; |
| 127 | + box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1); |
| 128 | + } |
| 129 | +
|
| 130 | + .card-title { |
| 131 | + margin: 0 0 12px 0; |
| 132 | + font-size: 1.25rem; |
| 133 | + font-weight: bold; |
| 134 | + } |
| 135 | +
|
| 136 | + .card-content { |
| 137 | + margin: 0; |
| 138 | + line-height: 1.5; |
| 139 | + color: #666; |
| 140 | + } |
| 141 | + </style> |
| 142 | + </head> |
| 143 | + <body> |
| 144 | + <div class="card"> |
| 145 | + <h3 class="card-title">Product Feature</h3> |
| 146 | + <p class="card-content"> |
| 147 | + This card demonstrates how the box model creates consistent spacing and |
| 148 | + structure in component-based designs. |
| 149 | + </p> |
| 150 | + </div> |
| 151 | + </body> |
| 152 | +</html> |
| 153 | +``` |
| 154 | + |
| 155 | +This generates the following output: |
| 156 | + |
| 157 | + |
| 158 | + |
| 159 | +This card example showcases practical box model usage where the padding creates comfortable internal spacing, the border defines the component boundary, and margins provide separation between multiple cards. The `max-width` property ensures responsive behavior while maintaining the box model calculations. |
| 160 | + |
| 161 | +## Example 3: Box-Sizing Property Control |
| 162 | + |
| 163 | +The following example illustrates the difference between `content-box` and `border-box` sizing models and their practical applications: |
| 164 | + |
| 165 | +```css |
| 166 | +.container { |
| 167 | + display: flex; |
| 168 | + gap: 20px; |
| 169 | + margin: 20px 0; |
| 170 | +} |
| 171 | + |
| 172 | +.content-box-example { |
| 173 | + box-sizing: content-box; /* Default behavior */ |
| 174 | + width: 200px; |
| 175 | + height: 100px; |
| 176 | + padding: 20px; |
| 177 | + border: 5px solid #e74c3c; |
| 178 | + background-color: #fadbd8; |
| 179 | +} |
| 180 | + |
| 181 | +.border-box-example { |
| 182 | + box-sizing: border-box; /* Alternative model */ |
| 183 | + width: 200px; /* Total width including padding and border */ |
| 184 | + height: 100px; /* Total height including padding and border */ |
| 185 | + padding: 20px; |
| 186 | + border: 5px solid #3498db; |
| 187 | + background-color: #d6eaf8; |
| 188 | +} |
| 189 | + |
| 190 | +/* Global border-box for consistent layouts */ |
| 191 | +*, |
| 192 | +*::before, |
| 193 | +*::after { |
| 194 | + box-sizing: border-box; |
| 195 | +} |
| 196 | +``` |
| 197 | + |
| 198 | +```html |
| 199 | +<!DOCTYPE html> |
| 200 | +<html lang="en"> |
| 201 | + <head> |
| 202 | + <meta charset="UTF-8" /> |
| 203 | + <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> |
| 204 | + <title>Box-Sizing Property Control</title> |
| 205 | + <style> |
| 206 | + .container { |
| 207 | + display: flex; |
| 208 | + gap: 20px; |
| 209 | + margin: 20px 0; |
| 210 | + } |
| 211 | +
|
| 212 | + .content-box-example { |
| 213 | + box-sizing: content-box; |
| 214 | + width: 200px; |
| 215 | + height: 100px; |
| 216 | + padding: 20px; |
| 217 | + border: 5px solid #e74c3c; |
| 218 | + background-color: #fadbd8; |
| 219 | + } |
| 220 | +
|
| 221 | + .border-box-example { |
| 222 | + box-sizing: border-box; |
| 223 | + width: 200px; |
| 224 | + height: 100px; |
| 225 | + padding: 20px; |
| 226 | + border: 5px solid #3498db; |
| 227 | + background-color: #d6eaf8; |
| 228 | + } |
| 229 | +
|
| 230 | + /* Global border-box for consistent layouts */ |
| 231 | + *, |
| 232 | + *::before, |
| 233 | + *::after { |
| 234 | + box-sizing: border-box; |
| 235 | + } |
| 236 | + </style> |
| 237 | + </head> |
| 238 | + <body> |
| 239 | + <div class="container"> |
| 240 | + <div class="content-box-example"> |
| 241 | + Content Box: Total width = 250px (200 + 40 + 10) |
| 242 | + </div> |
| 243 | + <div class="border-box-example"> |
| 244 | + Border Box: Total width = 200px (padding and border included) |
| 245 | + </div> |
| 246 | + </div> |
| 247 | + </body> |
| 248 | +</html> |
| 249 | +``` |
17 | 250 |
|
18 | | -- `width` and `height`: The width and height of the content area. |
19 | | -- `padding`: The amount of space between the content area and the border. |
20 | | -- `border`: The thickness and style of the border surrounding the content area and padding. |
21 | | -- `margin`: The amount of space between the border and the outside edge of the element. |
| 251 | +This generates the following output: |
22 | 252 |
|
23 | | - |
| 253 | +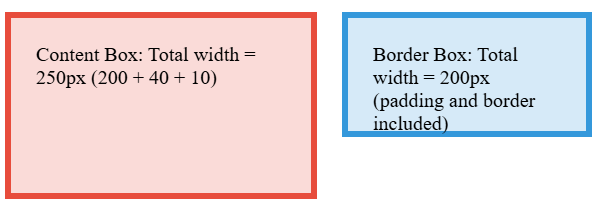 |
24 | 254 |
|
25 | | -## Content Area |
| 255 | +The `content-box` element has a total width of 250px because padding and border are added to the specified width. The `border-box` element maintains exactly 200px total width with padding and border calculated within that constraint. The global rule at the bottom applies `border-box` to all elements, which is a common practice for predictable layouts. |
26 | 256 |
|
27 | | -This area contains the actual content of an element, including text and images. It also sometimes has a `background-color` or `background-image`. |
| 257 | +## Frequently Asked Questions |
28 | 258 |
|
29 | | -## Padding Area |
| 259 | +### 1. What's the difference between padding and margin? |
30 | 260 |
|
31 | | -This area is located between the content and border areas. It can be changed on the top, right, bottom and left sides. |
| 261 | +Padding is the space inside an element between content and the border. A margin is the space outside the border that separates elements. |
32 | 262 |
|
33 | | -## Border Area |
| 263 | +### 2. Why do my element widths seem larger than expected? |
34 | 264 |
|
35 | | -This area is located between the margin and padding areas. Their thickness and style can be changed. |
| 265 | +By default, CSS adds padding and border to the specified width. Use `box-sizing: border-box` to include them within the width. |
36 | 266 |
|
37 | | -## Margin Area |
| 267 | +### 3. What happens if I set negative padding or margin? |
38 | 268 |
|
39 | | -This is the outermost area in the Box Model. It borders with the margin areas of neighboring elements. It can be changed on the top, right, bottom and left sides. |
| 269 | +Negative padding is invalid and ignored. Negative margins are valid and pull elements closer or cause overlap. |
0 commit comments