You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
Copy file name to clipboardExpand all lines: docs/administration/bpm-compensation.md
+5-7
Original file line number
Diff line number
Diff line change
@@ -2,11 +2,11 @@
2
2
3
3
*As of Advanced Pack v2.14.*
4
4
5
-
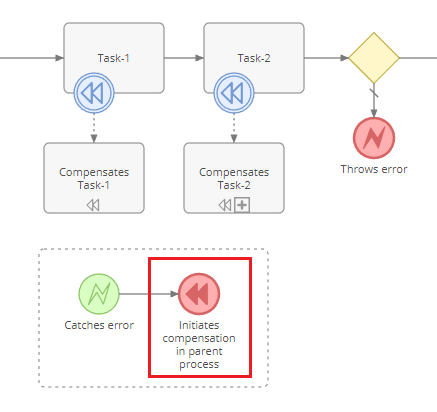
Compensation mechanism is supposed to perform undo actions when something went wrong. Only successfully completed activities can be compensated. Both tasks and sub-processes can be compensated.
5
+
The Compensation mechanism is supposed to perform undo actions when something went wrong. Only successfully completed activities can be compensated. Both tasks and sub-processes can be compensated.
6
6
7
-
Compensation is initiated by triggering a Compensation Event (usually from an error handler). The throwing compensation event can specify an activity's ID that needs to be compensated. If the ID is omitted, all *visible**compensable* activities will be compensated in the order reverse to their instantiation.
7
+
A compensation is initiated by triggering a Compensation Event (usually from an error handler). The throwing compensation event can specify an activity's ID that needs to be compensated. If the ID is omitted, all *visible**compensable* activities will be compensated in the order reverse to their instantiation.
8
8
9
-
By utilizing intermediate throwing compensation events it is possible to establish a specific order in which compensations will be executed.
9
+
By utilizing intermediate throwing compensation events, it is possible to establish a specific order in which compensations will be executed.
10
10
11
11
!!! note
12
12
@@ -23,15 +23,15 @@ Boundary compensation:
23
23
24
24
When a sub-process is compensated with the boundary event, the compensation activity does not have access to the sub-process internal state (called Black-Box compensation). To be able to access the internal state, use the Compensation Event Sub-Process inside the sub-process.
25
25
26
-
When the parent process initiates compensation for the sub-process activity, if there's no boundary compensation event attached to that activity, it will check whether the sub-process contains an event sub-process with a compensation start event (called Compensation Handler). Then it executes the compensation handler. The compensation handler usually is supposed to explicitly throw compensation events to compensate activities of the sub-process.
26
+
When the parent process initiates compensation for the sub-process activity, if there's no boundary compensation event attached to that activity, it will check whether the sub-process contains an event sub-process with a compensation start event (called Compensation Handler). Then, it executes the compensation handler. The compensation handler usually is supposed to explicitly throw compensation events to compensate activities of the sub-process.
An activity is considered **visible** from the throwing Event when:
33
33
34
-
* It is contained in normal flow at the same level of the process/sub-process.
34
+
* It is contained in a normal flow at the same level of the process/sub-process.
35
35
* It is contained in the parent process/sub-process of an event sub-process in which the Event is contained.
36
36
37
37
In the same level:
@@ -42,11 +42,9 @@ From the event sub-process:
42
42
43
43
0 commit comments