mirrord lets developers run local processes in the context of their cloud environment. It provides the benefits of running your service on a cloud environment (e.g. staging) without going through the hassle of deploying it there, and without disrupting the environment by deploying untested code. It comes as a Visual Studio Code extension, an IntelliJ plugin and a CLI tool. You can read more about what mirrord does in our official docs.
This repository is for the VSCode extension. mirrord's main repository can be found here.
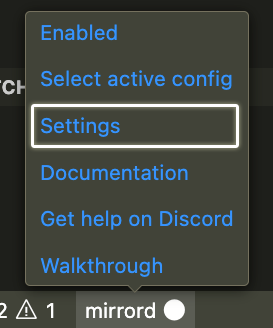
- Click the mirrord status bar item to switch mirrord from
DisabledtoEnabled
-
Start debugging your project (shortcut: F5)
-
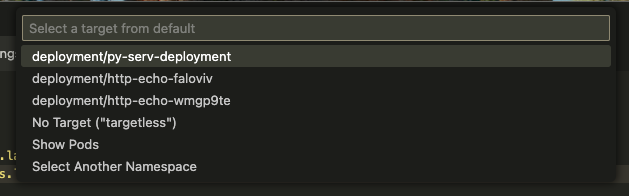
Choose a target to impersonate
- The debugged process will start with mirrord, and receive the context of the impersonated pod. It will receive its environment variables and incoming traffic, will read and write files to it, and send outgoing traffic through it.
Unless explicitly set in the config, mirrord uses your machine's default kubeconfig for access to the Kubernetes API. Alternatively, use the port mapping configuration.
For incoming traffic, make sure your local process is listening on the same port as the remote pod.
mirrord allows for rich configuration of the environment it provides. The schema for it is documented here. The extension supports autocomplete for json files, but you can also use toml or yaml format.
Quick start: the easiest way to start configuring mirrord is to choose "Settings" from the status bar menu, which will open a new mirrord.json.
- Feel free to join to our Discord channel if you need help using mirrord, or if you encounter an issue while using the extension.
- Check our open issues for the VSCode extension and mirrord's core code, and 👍 react to any that you would like to see addressed.
- Before submitting a pull request for new features, please take a look at mirrord's contributing guide.